Business Models
EDIFICE created a set of Business Information Modeling (BIM) Guidelines in the following Business areas:
| DISTRIBUTION CHANNEL Management – Version 5.0 Publication Date 09-06-2010 | |
| This document describes the business processes and information flows in the area of Distribution Channel Management (DCM).The goal is to provide a reference document which allows for consistent implementation of such processes within the electronics industry. The prime focus is on the B2B aspects. The scenarios included concern: Price Catalog; Quotation; Design Win; … | |
| FORECAST & INVENTORY MANAGEMENT – Version 2.0 Publication Date 05-08-2003 | |
| Business Model GUIDELINE - Forecast & Inventory Management | The models below describe various business scenarios in which forecast, order and inventory information may be exchanged between buyer (customer) and seller (supplier), for various business purposes including forecasting, planning, delivery scheduling and inventory management between the involved parties.The specification of business processes and information flows forms part of the EDIFICE EDI Implementation guideline, and describes contexts in which the EDIFICE Delivery Forecast, Delivery Just In Time and Inventory Report EDI messages are intended to be used. These activities do not operate independently of other processes: conventional ordering, invoicing/self-billing, physical distribution and payment processes may also be involved. |
| PHYSICAL DISTRIBUTION – Version 1.0 Publication Date 29-11-1995 | |
| Business Model Guideline - Physical Distribution | In the Physical Distribution business area, the entities that are linked together within the supply chain are highlighted in the following diagram.The flows and interactions among the physical entities vary according to the trade area (international, domestic or within the European Union), and the trade terms. The diagram shows all the possible links. Each enterprise is described in section 1.2 and the various linkages are explained in section 1.3. Section 3 of the document details the interactions under different trading scenarios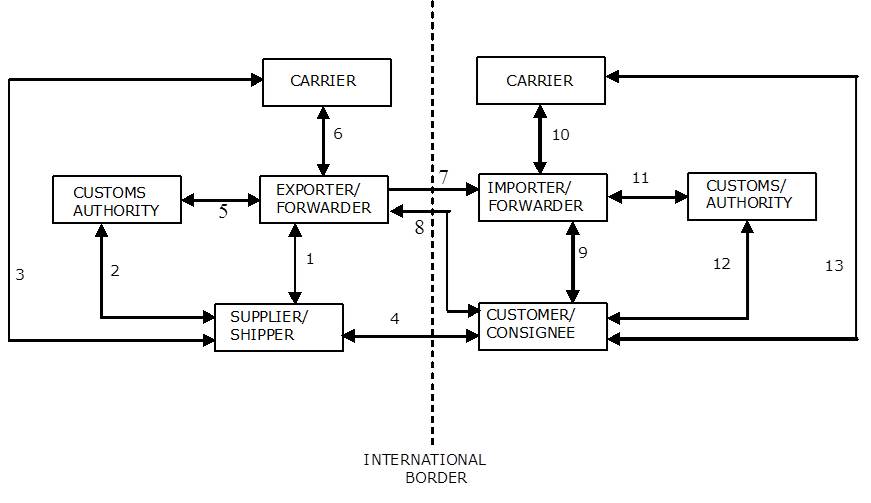 |
| SELF-BILLING – Version 2.0 Publication Date 29-05-2002 | |
| Business Model Guideline - Self-Billing Invoice | The self-billing process is a re-engineering effort, based on the traditional invoice process, associated with liability settlements arising from supply of goods between customer and supplier. Self-billing is the procedure for authorising payment for received goods based on received or used quantities of goods. Prices must be pre-negotiated and maintained by both the customer and the supplier in their respective applications in order for the process to operate smoothly.This document describes two distinct business scenarios where self-billing is used: Evaluated Receipt Settlement (ERS) (section 3.1) Consignment stock (section 3.2)… |
